- Configuring LinuxCNC
- Configuration Tools
- PnCConf Wizard
- correspondence of unused i/o pins to physical connector location?
correspondence of unused i/o pins to physical connector location?
- pgf
- Offline
- Premium Member
-
Less
More
- Posts: 125
- Thank you received: 23
24 Mar 2025 12:14 #324744
by pgf
correspondence of unused i/o pins to physical connector location? was created by pgf
Is there a chart somewhere that correlates the 3 digit I/O number shown in pncconf with their physical terminal on the board? I assume those 3 digit numbers are a number used by the firmware to represent the pin, but on the board, by the time you try and subtract out the power and ground pins, and try and figure out how many actual I/O pins an encoder or serial port uses, it's almost impossible to tell what's being configured. I've been trying to compare with the board drawing from the Mesa 7i96 manual, and also with the actual board, and I'm coming up empty.
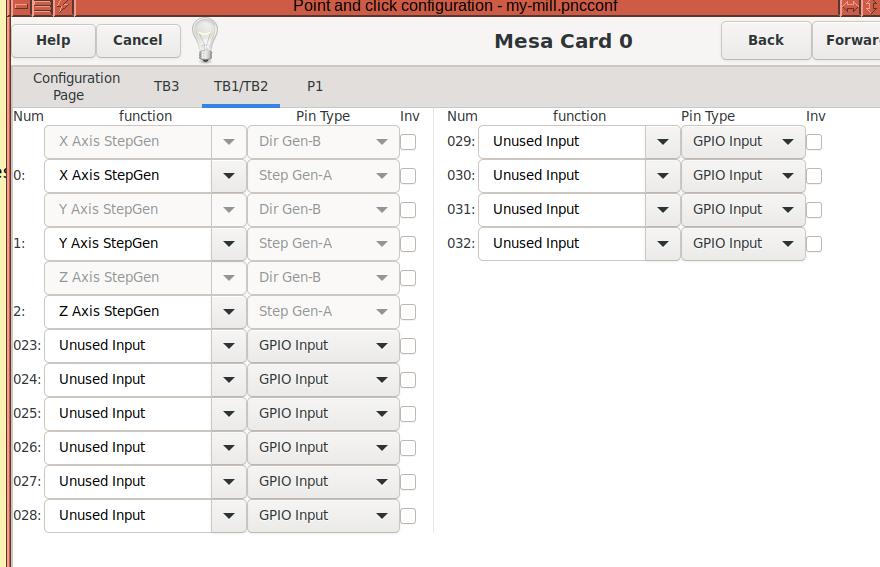
I'm referring to the 023 to 032 numbers in this screenshot.
I'm referring to the 023 to 032 numbers in this screenshot.
Attachments:
Please Log in or Create an account to join the conversation.
- rodw
-

- Offline
- Platinum Member
-
Less
More
- Posts: 11722
- Thank you received: 3968
24 Mar 2025 12:23 #324745
by rodw
Replied by rodw on topic correspondence of unused i/o pins to physical connector location?
The mesa manual for your card outlines it all.
the physical pins are generally numbered from 1 but the pin numbers start with 0
the physical pins are generally numbered from 1 but the pin numbers start with 0
Please Log in or Create an account to join the conversation.
- unknown
- Offline
- Platinum Member
-
Less
More
- Posts: 888
- Thank you received: 325
24 Mar 2025 12:47 #324748
by unknown
Replied by unknown on topic correspondence of unused i/o pins to physical connector location?
The .pin file in the firmware package has that info (if you know the firmware it was programmed with) or you can use mesaflash with the readhmid command (after adding the address & such)
example 7i96_5abob_d.pin file for 7i96 if programmed with 7i96_5abob_d.bit file
example 7i96_5abob_d.pin file for 7i96 if programmed with 7i96_5abob_d.bit file
Configuration Name: HOSTMOT2
General configuration information:
BoardName : MESA7I96
FPGA Size: 9 KGates
FPGA Pins: 144
Number of IO Ports: 3
Width of one I/O port: 17
Clock Low frequency: 100.0000 MHz
Clock High frequency: 200.0000 MHz
IDROM Type: 3
Instance Stride 0: 4
Instance Stride 1: 64
Register Stride 0: 256
Register Stride 1: 256
Modules in configuration:
Module: DPLL
There are 1 of DPLL in configuration
Version: 0
Registers: 7
BaseAddress: 7000
ClockFrequency: 100.000 MHz
Register Stride: 256 bytes
Instance Stride: 4 bytes
Module: WatchDog
There are 1 of WatchDog in configuration
Version: 0
Registers: 3
BaseAddress: 0C00
ClockFrequency: 100.000 MHz
Register Stride: 256 bytes
Instance Stride: 4 bytes
Module: IOPort
There are 3 of IOPort in configuration
Version: 0
Registers: 5
BaseAddress: 1000
ClockFrequency: 100.000 MHz
Register Stride: 256 bytes
Instance Stride: 4 bytes
Module: PWM
There are 1 of PWM in configuration
Version: 0
Registers: 5
BaseAddress: 4100
ClockFrequency: 200.000 MHz
Register Stride: 256 bytes
Instance Stride: 4 bytes
Module: StepGen
There are 8 of StepGen in configuration
Version: 2
Registers: 10
BaseAddress: 2000
ClockFrequency: 100.000 MHz
Register Stride: 256 bytes
Instance Stride: 4 bytes
Module: QCount
There are 2 of QCount in configuration
Version: 2
Registers: 5
BaseAddress: 3000
ClockFrequency: 100.000 MHz
Register Stride: 256 bytes
Instance Stride: 4 bytes
Module: SSerial
There are 1 of SSerial in configuration
Version: 0
Registers: 6
BaseAddress: 5B00
ClockFrequency: 100.000 MHz
Register Stride: 256 bytes
Instance Stride: 64 bytes
Module: SSR
There are 1 of SSR in configuration
Version: 0
Registers: 2
BaseAddress: 7D00
ClockFrequency: 100.000 MHz
Register Stride: 256 bytes
Instance Stride: 4 bytes
Module: LED
There are 1 of LED in configuration
Version: 0
Registers: 1
BaseAddress: 0200
ClockFrequency: 100.000 MHz
Register Stride: 256 bytes
Instance Stride: 4 bytes
Configuration pin-out:
IO Connections for TB3
Pin# I/O Pri. func Sec. func Chan Pin func Pin Dir
1 0 IOPort None
14 1 IOPort None
2 2 IOPort None
15 3 IOPort None
3 4 IOPort None
16 5 IOPort None
4 6 IOPort None
17 7 IOPort None
5 8 IOPort None
6 9 IOPort None
7 10 IOPort None
8 11 IOPort SSR 0 Out-00 (Out)
9 12 IOPort SSR 0 Out-01 (Out)
10 13 IOPort SSR 0 Out-02 (Out)
11 14 IOPort SSR 0 Out-03 (Out)
12 15 IOPort SSR 0 Out-04 (Out)
13 16 IOPort SSR 0 Out-05 (Out)
IO Connections for TB1/TB2
Pin# I/O Pri. func Sec. func Chan Pin func Pin Dir
1 17 IOPort StepGen 0 Step/Table1 (Out)
14 18 IOPort StepGen 0 Dir/Table2 (Out)
2 19 IOPort StepGen 1 Step/Table1 (Out)
15 20 IOPort StepGen 1 Dir/Table2 (Out)
3 21 IOPort StepGen 2 Step/Table1 (Out)
16 22 IOPort StepGen 2 Dir/Table2 (Out)
4 23 IOPort StepGen 3 Step/Table1 (Out)
17 24 IOPort StepGen 3 Dir/Table2 (Out)
5 25 IOPort StepGen 4 Step/Table1 (Out)
6 26 IOPort StepGen 4 Dir/Table2 (Out)
7 27 IOPort QCount 0 Quad-A (In)
8 28 IOPort QCount 0 Quad-B (In)
9 29 IOPort QCount 0 Quad-IDX (In)
10 30 IOPort SSerial 0 RXData0 (In)
11 31 IOPort SSerial 0 TXData0 (Out)
12 32 IOPort SSerial 0 TXEn0 (Out)
13 33 IOPort SSR 0 AC Ref (Out)
IO Connections for P1
Pin# I/O Pri. func Sec. func Chan Pin func Pin Dir
1 34 IOPort PWM 0 PWM (Out)
14 35 IOPort None
2 36 IOPort StepGen 5 Step/Table1 (Out)
15 37 IOPort None
3 38 IOPort StepGen 5 Dir/Table2 (Out)
16 39 IOPort None
4 40 IOPort StepGen 6 Step/Table1 (Out)
17 41 IOPort None
5 42 IOPort StepGen 6 Dir/Table2 (Out)
6 43 IOPort StepGen 7 Step/Table1 (Out)
7 44 IOPort StepGen 7 Dir/Table2 (Out)
8 45 IOPort None
9 46 IOPort None
10 47 IOPort None
11 48 IOPort QCount 1 Quad-A (In)
12 49 IOPort QCount 1 Quad-B (In)
13 50 IOPort QCount 1 Quad-IDX (In)Please Log in or Create an account to join the conversation.
- pgf
- Offline
- Premium Member
-
Less
More
- Posts: 125
- Thank you received: 23
24 Mar 2025 13:16 #324760
by pgf
www.mesanet.com/pdf/parallel/7i96man.pdf
Replied by pgf on topic correspondence of unused i/o pins to physical connector location?
No, I don't think it does. It does have that info for the P1 expansion connector, but not for TB1 and TB2.The mesa manual for your card outlines it all.
the physical pins are generally numbered from 1 but the pin numbers start with 0
www.mesanet.com/pdf/parallel/7i96man.pdf
Please Log in or Create an account to join the conversation.
- pgf
- Offline
- Premium Member
-
Less
More
- Posts: 125
- Thank you received: 23
24 Mar 2025 13:19 #324764
by pgf
Replied by pgf on topic correspondence of unused i/o pins to physical connector location?
Thank you -- I haven't run my own test yet, but I see the correlations in your sample output.
If I were a python or gui programmer, I'd take a stab at adding that info to pncconf. And I suppose I'd probably discover that it's difficult, which is why it hasn't been done.
Seems like there should be an easier way, than by powering up the board you're trying to configure!
paul
If I were a python or gui programmer, I'd take a stab at adding that info to pncconf. And I suppose I'd probably discover that it's difficult, which is why it hasn't been done.
Seems like there should be an easier way, than by powering up the board you're trying to configure!
paul
Please Log in or Create an account to join the conversation.
- unknown
- Offline
- Platinum Member
-
Less
More
- Posts: 888
- Thank you received: 325
24 Mar 2025 13:28 #324769
by unknown
Replied by unknown on topic correspondence of unused i/o pins to physical connector location?
If you know what firmware you have on board, eg the name of the .bit file, all you need to is look in the corresponding pin file, if you've downloaded the firmware stuff.
If not you can redirect the mesaflash output to a text file.
Don't mind me I still spend a bit of time using the command line in Linux. Just find it can be a bit quicker at times.
If not you can redirect the mesaflash output to a text file.
Don't mind me I still spend a bit of time using the command line in Linux. Just find it can be a bit quicker at times.
Please Log in or Create an account to join the conversation.
- pgf
- Offline
- Premium Member
-
Less
More
- Posts: 125
- Thank you received: 23
24 Mar 2025 13:33 #324772
by pgf
Replied by pgf on topic correspondence of unused i/o pins to physical connector location?
I don't actually know what firmware I have, nor have I downloaded any. I assumed it shipped with the firmware I need.
The manual corresponds to a specific firmware, no? So the information could/should be in the manual.
The manual corresponds to a specific firmware, no? So the information could/should be in the manual.
Please Log in or Create an account to join the conversation.
- unknown
- Offline
- Platinum Member
-
Less
More
- Posts: 888
- Thank you received: 325
24 Mar 2025 13:48 #324775
by unknown
Replied by unknown on topic correspondence of unused i/o pins to physical connector location?
There's so many different configs available, and you can even build your own firmware from source. So the manual is pretty generic.
Off track
I haven't use the 7i96, I have a 7i92/7i76 for the mill, with a couple of extra boards, I've hacked to together some FPGA dev boards to use self built 7c81/7i90 firmware. SPI & EPP is easy pcb wise, but I'm having a go at a board using ethernet based on the 7i92 schematics.
On Track
The mesa hardware & firmware is really versatile. Actually the 7i90 would be a great way to learn to program FPGAs as the I\O is 5v tolerant, most dev boards are only good for 3.3v or the smoke comes out.
Off track
I haven't use the 7i96, I have a 7i92/7i76 for the mill, with a couple of extra boards, I've hacked to together some FPGA dev boards to use self built 7c81/7i90 firmware. SPI & EPP is easy pcb wise, but I'm having a go at a board using ethernet based on the 7i92 schematics.
On Track
The mesa hardware & firmware is really versatile. Actually the 7i90 would be a great way to learn to program FPGAs as the I\O is 5v tolerant, most dev boards are only good for 3.3v or the smoke comes out.
Please Log in or Create an account to join the conversation.
- pgf
- Offline
- Premium Member
-
Less
More
- Posts: 125
- Thank you received: 23
24 Mar 2025 13:57 #324776
by pgf
mesaflash has provided me with the table I wanted.
Replied by pgf on topic correspondence of unused i/o pins to physical connector location?
No need to apologize. I've been working at Unix/Linux command line prompts since 1980.If not you can redirect the mesaflash output to a text file.
Don't mind me I still spend a bit of time using the command line in Linux. Just find it can be a bit quicker at times.
mesaflash has provided me with the table I wanted.
Please Log in or Create an account to join the conversation.
- pgf
- Offline
- Premium Member
-
Less
More
- Posts: 125
- Thank you received: 23
24 Mar 2025 14:04 #324777
by pgf
Replied by pgf on topic correspondence of unused i/o pins to physical connector location?
Although, I don't understand why the pin func for the Stepgens are all "Step/Table1" and "Dir/Table2". I would have expected an index between 1 and 5 (or 0 and 4).
IO Connections for TB1/TB2 -> 7I96_1
Pin# I/O Pri. func Sec. func Sec. Pin func Sec. Pin Dir
TB1-2,3 17 IOPort StepGen Step/Table1 (Out)
TB1-4,5 18 IOPort StepGen Dir/Table2 (Out)
TB1-8,9 19 IOPort StepGen Step/Table1 (Out)
TB1-10,11 20 IOPort StepGen Dir/Table2 (Out)
TB1-14,15 21 IOPort StepGen Step/Table1 (Out)
TB1-16,17 22 IOPort StepGen Dir/Table2 (Out)
TB1-20,21 23 IOPort StepGen Step/Table1 (Out)
TB1-22,23 24 IOPort StepGen Dir/Table2 (Out)
TB2-2,3 25 IOPort StepGen Step/Table1 (Out)
TB2-4,5 26 IOPort StepGen Dir/Table2 (Out)
TB2-7,8 27 IOPort QCount Quad-A (In)
TB2-10,11 28 IOPort QCount Quad-B (In)
TB2-13,14 29 IOPort QCount Quad-IDX (In)
TB2-16,17 30 IOPort SSerial RXData0 (In)
TB2-18,19 31 IOPort SSerial TXData0 (Out)
Internal-TXEn 32 IOPort SSerial TXEn0 (Out)
Internal 33 IOPort SSR AC Ref (Out)
Please Log in or Create an account to join the conversation.
Moderators: cmorley
- Configuring LinuxCNC
- Configuration Tools
- PnCConf Wizard
- correspondence of unused i/o pins to physical connector location?
Time to create page: 0.294 seconds