Search Results (Searched for: )
- rodw

21 Feb 2025 10:48
Replied by rodw on topic Building a 3-axis plasma table with mesa 7i96s, THCad-2 and nema23 steppers
Building a 3-axis plasma table with mesa 7i96s, THCad-2 and nema23 steppers
Category: Show Your Stuff
I've not used it in earnest but QTplasmac installs fine with 4 axes with 2 motors on the gantry, XYYZA
I have installed it with 5 stepper drives though
Probably pair it up with Sheetcam rotary for CAM
I have installed it with 5 stepper drives though
Probably pair it up with Sheetcam rotary for CAM
- Daan96
- Daan96
21 Feb 2025 10:31
Replied by Daan96 on topic Building a 3-axis plasma table with mesa 7i96s, THCad-2 and nema23 steppers
Building a 3-axis plasma table with mesa 7i96s, THCad-2 and nema23 steppers
Category: Show Your Stuff
Then the choice seems quickly made; I'll have to get my hands on an old PC and start exploring Linux, which is completely new to me. Do you have it running on an old PC mounted near the table, or is it also possible to run Linux on a NUC?
In any case, I'll dive into the various posts on this forum while continuing with the mechanical design.
I see that QTPlasm doesn't work so easily for the rotation axis—perhaps I should leave it out for the first project and later build it as a standalone machine, just like Tommy did.
Thanks for the input! It's greatly appreciated!
In any case, I'll dive into the various posts on this forum while continuing with the mechanical design.
I see that QTPlasm doesn't work so easily for the rotation axis—perhaps I should leave it out for the first project and later build it as a standalone machine, just like Tommy did.
Thanks for the input! It's greatly appreciated!
- JuFu
- JuFu
21 Feb 2025 10:16
Switching HAL pin in subroutine (macro) was created by JuFu
Switching HAL pin in subroutine (macro)
Category: O Codes (subroutines) and NGCGUI
I want to set / reset a HAL pin by using G-codes (switching a pneumatic valve on/off).
In the documentation G-code Overview | 4. HAL pins and INI values is written: " ... the only way to set HAL pins from G-code remains M62-M65, M67, M68 and custom M100-M199 codes."
I wrote the below subroutine (macro):
o<test> sub
(MSG, Spannzange öffnen)
M62 #<_hal[hm2_7i76e.0.7i76.0.0.output-00]
o<test> endsub
M2
When I run the macro, the response is: "Benannter Parameter nicht beendet"
(Using gmoccapy Ver 3.4.9 in German language)
Is there a better way to control HAL pins?
If not, what do I need to do?
Juergen
In the documentation G-code Overview | 4. HAL pins and INI values is written: " ... the only way to set HAL pins from G-code remains M62-M65, M67, M68 and custom M100-M199 codes."
I wrote the below subroutine (macro):
o<test> sub
(MSG, Spannzange öffnen)
M62 #<_hal[hm2_7i76e.0.7i76.0.0.output-00]
o<test> endsub
M2
When I run the macro, the response is: "Benannter Parameter nicht beendet"
(Using gmoccapy Ver 3.4.9 in German language)
Is there a better way to control HAL pins?
If not, what do I need to do?
Juergen
- Grotius

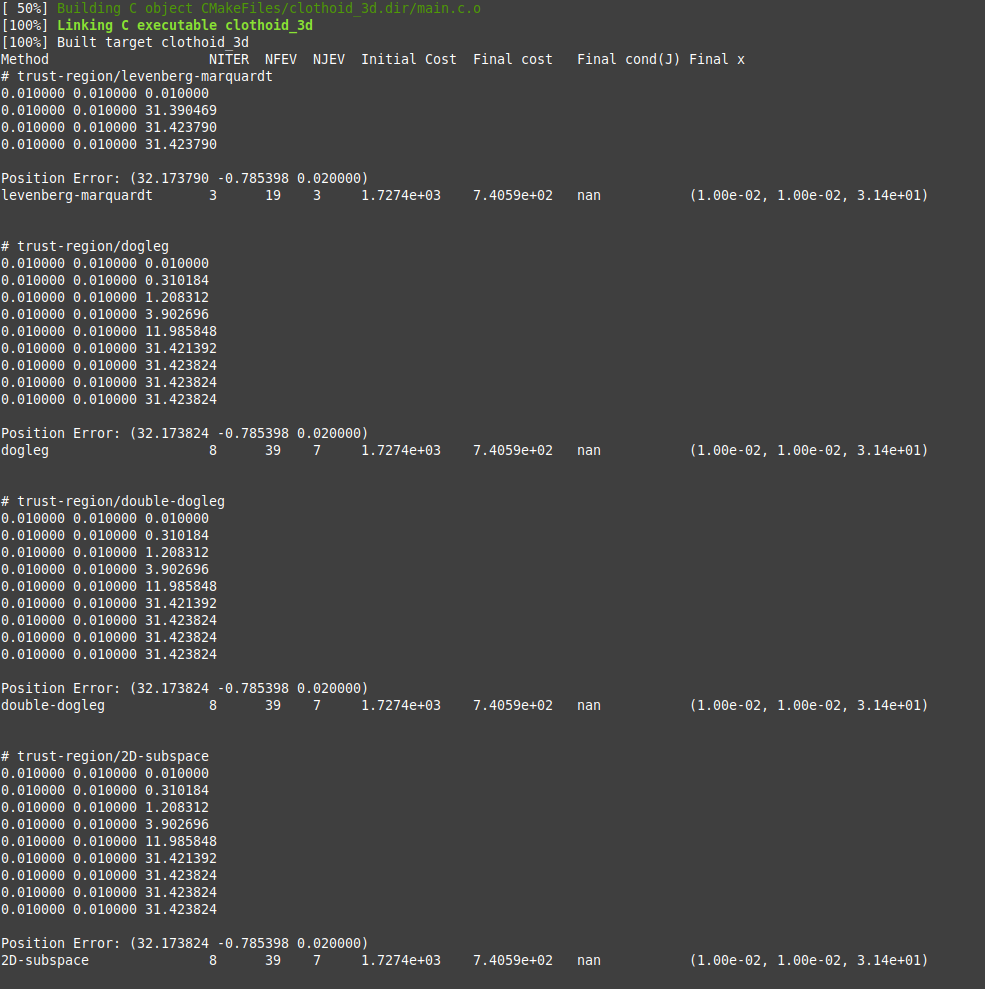
21 Feb 2025 10:10 - 21 Feb 2025 13:04
Replied by Grotius on topic scurve trajectory planner
scurve trajectory planner
Category: General LinuxCNC Questions
@Arciera,
That's what i think we don't need. If the dogleg solver is able to find the endpoint in 3d space. Why do the tranformations
as used in the abstract?
We have already a case where the helix tail or start from a G2, G3 is used as end vector.
I see you have splitted up the gaus interpolation into x, y, z.
Edit:
Did a mayor update on the infrastructure.
- Use struct for clothoid data.
- Use seperate plot function.
- Use enum to choose a solver from the list.
- Use a central residual function used by all solvers. Where the objective function can cast types.
That's what i think we don't need. If the dogleg solver is able to find the endpoint in 3d space. Why do the tranformations
as used in the abstract?
We have already a case where the helix tail or start from a G2, G3 is used as end vector.
I see you have splitted up the gaus interpolation into x, y, z.
Edit:
Did a mayor update on the infrastructure.
- Use struct for clothoid data.
- Use seperate plot function.
- Use enum to choose a solver from the list.
- Use a central residual function used by all solvers. Where the objective function can cast types.
- Aciera

21 Feb 2025 10:06
Replied by Aciera on topic scurve trajectory planner
scurve trajectory planner
Category: General LinuxCNC Questions
As i understand it there should be no need for another transformation besides the one described in the paper.
- JB-Motoring
- JB-Motoring
21 Feb 2025 10:00
Replied by JB-Motoring on topic Mesa 7i97T + 7i84 + 7i78 configuration
Mesa 7i97T + 7i84 + 7i78 configuration
Category: General LinuxCNC Questions
Hey guys,
so I got Linuxcnc running- And I would like to test all i o 's on the bench before moving to the machine.
As soon as I hit enable (F1/F2) all assigned Analog Outputs show -10V.
There is no encoder or drive connected, just the naked Mesa on the desk.
How can I handle this to see, if the output is working?
Thanks guys!
so I got Linuxcnc running- And I would like to test all i o 's on the bench before moving to the machine.
As soon as I hit enable (F1/F2) all assigned Analog Outputs show -10V.
There is no encoder or drive connected, just the naked Mesa on the desk.
How can I handle this to see, if the output is working?
Thanks guys!
- Grotius

21 Feb 2025 09:58
Replied by Grotius on topic scurve trajectory planner
scurve trajectory planner
Category: General LinuxCNC Questions
@Arciera,
Indeed. Good spot !!!
I was thinking about the 3d fitting between gcode segments.
Do we really need the transformation, and then do the fitting in a null plane?
This was needed for a 2d clothoid, when used in a 3d plane. But for this i think
we don't needed, unless there is something i forgot.
I thought maybe we can just fit the clothoids in 3d space.
Indeed. Good spot !!!
I was thinking about the 3d fitting between gcode segments.
Do we really need the transformation, and then do the fitting in a null plane?
This was needed for a 2d clothoid, when used in a 3d plane. But for this i think
we don't needed, unless there is something i forgot.
I thought maybe we can just fit the clothoids in 3d space.
- Aciera

21 Feb 2025 09:56
Replied by Aciera on topic scurve trajectory planner
scurve trajectory planner
Category: General LinuxCNC Questions
Here is my failed attempt:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_vector.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_matrix.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_blas.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_multifit_nlinear.h>
/* eq18, page 4.
*
* stot = total clothoid length
* s = global length at clothoid to retrieve sharpness c.
*
* Retrieve the sharpness for s.
*
*/
void eq18(const double s, const double stot,
const double sharpnessi0, const double sharpnessi1, const double sharpnessi2, const double sharpnessi3,
const double yi1, const double yi2, const double yi3, const double yi4,
double *sharpness_at_s) {
double s1 = stot / 4.0;
double s2 = s1 + s1;
double s3 = s1 + s1 + s1;
double s4 = stot;
if (s <= s1) {
*sharpness_at_s = sharpnessi0 + yi1 * s;
} else if (s > s1 && s <= s2) {
*sharpness_at_s = sharpnessi1 + yi2 * (s - s1);
} else if (s > s2 && s <= s3) {
*sharpness_at_s = sharpnessi2 + yi3 * (s - s2);
} else if (s > s3 && s <= s4) {
*sharpness_at_s = sharpnessi3 + yi4 * (s - s3);
} else {
// Handle the case where s is out of bounds (optional)
*sharpness_at_s = 0.0; // or some other default value
printf("error: eq18. \n");
}
}
void eq18_single_clothoid(const double s,
const double sharpnessi0,
const double yi1,
double *sharpness_at_s) {
*sharpness_at_s = sharpnessi0 + yi1 * s;
}
/* eq19, page 4.
*
* stot = total clothoid length
* s = global length at clothoid to retrieve sharpness c.
*
* Retrieve the kappa for s.
*
*/
void eq19(const double s, const double stot,
const double sharpnessi0, const double sharpnessi1, const double sharpnessi2, const double sharpnessi3,
const double kappai0, const double kappai1, const double kappai2, const double kappai3,
const double yi1, const double yi2, const double yi3, const double yi4,
double *kappa_at_s) {
double s1 = stot / 4.0;
double s2 = s1 + s1;
double s3 = s1 + s1 + s1;
double s4 = stot;
if (s <= s1) {
*kappa_at_s = kappai0 + sharpnessi0 * s + 0.5 * yi1 * (s * s);
} else if (s > s1 && s <= s2) {
*kappa_at_s = kappai1 + sharpnessi1 * (s - s1) + 0.5 * yi2 * ((s - s1) * (s - s1));
} else if (s > s2 && s <= s3) {
*kappa_at_s = kappai2 + sharpnessi2 * (s - s2) + 0.5 * yi3 * ((s - s2) * (s - s2));
} else if (s > s3 && s <= s4) {
*kappa_at_s = kappai3 + sharpnessi3 * (s - s3) + 0.5 * yi4 * ((s - s3) * (s - s3));
} else {
// Handle the case where s is out of bounds (optional)
*kappa_at_s = 0.0; // or some other default value
printf("error: eq19. \n");
}
}
void eq19_single_clothoid(const double s,
const double sharpnessi0,
const double kappai0,
const double yi1,
double *kappa_at_s) {
*kappa_at_s = kappai0 + sharpnessi0 * s + 0.5 * yi1 * (s * s);
}
/* eq20, page 4.
*
* stot = total clothoid length
* s = global length at clothoid to retrieve sharpness c.
*
* Retrieve the theta at s.
*
*/
void eq20(const double s, const double stot,
const double sharpnessi0, const double sharpnessi1, const double sharpnessi2, const double sharpnessi3,
const double kappai0, const double kappai1, const double kappai2, const double kappai3,
const double thetai0, const double thetai1, const double thetai2, const double thetai3,
const double yi1, const double yi2, const double yi3, const double yi4,
double *theta_at_s) {
double s1 = stot / 4.0;
double s2 = s1 + s1;
double s3 = s1 + s1 + s1;
double s4 = stot;
if (s <= s1) {
*theta_at_s = thetai0 + kappai0 * s + (0.5*sharpnessi0) * (s * s) + (1.0 / 6.0) * yi1 * (s * s * s);
} else if (s > s1 && s <= s2) {
*theta_at_s = thetai1 + kappai1 * (s - s1) + (0.5*sharpnessi1) * ((s - s1) * (s - s1)) + (1.0 / 6.0) * yi2 * ((s - s1) * (s - s1) * (s - s1));
} else if (s > s2 && s <= s3) {
*theta_at_s = thetai2 + kappai2 * (s - s2) + (0.5*sharpnessi2) * ((s - s2) * (s - s2)) + (1.0 / 6.0) * yi3 * ((s - s2) * (s - s2) * (s - s2));
} else if (s > s3 && s <= s4) {
*theta_at_s = thetai3 + kappai3 * (s - s3) + (0.5*sharpnessi3) * ((s - s3) * (s - s3)) + (1.0 / 6.0) * yi4 * ((s - s3) * (s - s3) * (s - s3));
} else {
// Handle the case where s is out of bounds (optional)
*theta_at_s = 0.0; // or some other default value
printf("error: eq20.\n");
}
}
/* Get the theta given s (length) for a single clothoid.
*
*/
void eq20_single_clothoid(const double s,
const double sharpnessi0,
const double kappai0,
const double thetai0,
const double yi1,
double *theta_at_s) {
*theta_at_s = thetai0 + kappai0 * s + (0.5*sharpnessi0) * (s * s) + (1.0 / 6.0) * yi1 * (s * s * s);
}
/* parameters to model */
struct model_params
{
double t10;
double t20;
double k10;
double k20;
double c10;
double c20;
double xs;
double ys;
double zs;
double xe;
double ye;
double ze;
double xi;
double yi;
double zi;
};
/* eq14, page 4
*
* Most efficient and precise solution to compute the clothoid curve lenght.
* Using gauss legendre, up to 20 points. Use a 30 point legendre to get even
* more accuracy.
*
* This calculation is more accurate then the above eq14_drift function.
*
* s = lenght on clothoid to retrieve the xyz point, xi,yi,zi.
* x0 y0 z0 = Clothoid start point.
* ltot = Clothoid length up to s.
*
* gamma1, gamma2, clothoid's rigid body factor. Synonims for y11, y22.
*
*/
float eq14_gauss_x(double s,
double x0, double xe,
double theta10, double theta20,
double kappa10, double kappa20,
double sharpness10, double sharpness20,
double gamma1, double gamma2) {
// Gauss-Legendre 20-point weights & nodes
const double gauss_weights[20] = {
0.1527533871, 0.1491729865, 0.1420961093, 0.1316886384, 0.1181945319,
0.1019301198, 0.0832767416, 0.0626720483, 0.0406014298, 0.0176140071,
0.0176140071, 0.0406014298, 0.0626720483, 0.0832767416, 0.1019301198,
0.1181945319, 0.1316886384, 0.1420961093, 0.1491729865, 0.1527533871
};
const double gauss_nodes[20] = {
-0.9931285992, -0.9639719273, -0.9122344283, -0.8391169718, -0.7463319065,
-0.6360536807, -0.5108670019, -0.3737060887, -0.2277858511, -0.0765265211,
0.0765265211, 0.2277858511, 0.3737060887, 0.5108670019, 0.6360536807,
0.7463319065, 0.8391169718, 0.9122344283, 0.9639719273, 0.9931285992
};
double sum_x = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
double weight = 0.5 * s * gauss_weights;
// Calculate the clothoid theta, kappa, sharpness at current s.
double sharpness10_i;
eq18_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10,gamma1,&sharpness10_i);
double sharpness20_i;
eq18_single_clothoid(0,sharpness20,gamma2,&sharpness20_i);
double kappa10_i;
eq19_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10_i,kappa10_i,gamma1,&kappa10_i);
double kappa20_i;
eq19_single_clothoid(0,sharpness20_i,kappa20_i,gamma2,&kappa20_i);
double theta10_i;
eq20_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10_i,kappa10_i,theta10,gamma1,&theta10_i);
double theta20_i;
eq20_single_clothoid(0,sharpness20_i,kappa20_i,theta20,gamma2,&theta20_i);
// Compute new coordinates using Gauss quadrature integration
double dx = cos(theta10_i) * cos(theta20_i) * weight;
sum_x += dx;
}
return x0 + sum_x - xe;
}
float eq14_gauss_y(double s,
double y0, double ye,
double theta10, double theta20,
double kappa10, double kappa20,
double sharpness10, double sharpness20,
double gamma1, double gamma2) {
// Gauss-Legendre 20-point weights & nodes
const double gauss_weights[20] = {
0.1527533871, 0.1491729865, 0.1420961093, 0.1316886384, 0.1181945319,
0.1019301198, 0.0832767416, 0.0626720483, 0.0406014298, 0.0176140071,
0.0176140071, 0.0406014298, 0.0626720483, 0.0832767416, 0.1019301198,
0.1181945319, 0.1316886384, 0.1420961093, 0.1491729865, 0.1527533871
};
const double gauss_nodes[20] = {
-0.9931285992, -0.9639719273, -0.9122344283, -0.8391169718, -0.7463319065,
-0.6360536807, -0.5108670019, -0.3737060887, -0.2277858511, -0.0765265211,
0.0765265211, 0.2277858511, 0.3737060887, 0.5108670019, 0.6360536807,
0.7463319065, 0.8391169718, 0.9122344283, 0.9639719273, 0.9931285992
};
double sum_y = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
double weight = 0.5 * s * gauss_weights;
// Calculate the clothoid theta, kappa, sharpness at current s.
double sharpness10_i;
eq18_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10,gamma1,&sharpness10_i);
double sharpness20_i;
eq18_single_clothoid(0,sharpness20,gamma2,&sharpness20_i);
double kappa10_i;
eq19_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10_i,kappa10_i,gamma1,&kappa10_i);
double kappa20_i;
eq19_single_clothoid(0,sharpness20_i,kappa20_i,gamma2,&kappa20_i);
double theta10_i;
eq20_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10_i,kappa10_i,theta10,gamma1,&theta10_i);
double theta20_i;
eq20_single_clothoid(0,sharpness20_i,kappa20_i,theta20,gamma2,&theta20_i);
// Compute new coordinates using Gauss quadrature integration
double dy = cos(theta10_i) * sin(theta20_i) * weight;
sum_y += dy;
}
return y0 + sum_y - ye;
}
float eq14_gauss_z(double s,
double z0, double ze,
double theta10, double theta20,
double kappa10, double kappa20,
double sharpness10, double sharpness20,
double gamma1, double gamma2) {
// Gauss-Legendre 20-point weights & nodes
const double gauss_weights[20] = {
0.1527533871, 0.1491729865, 0.1420961093, 0.1316886384, 0.1181945319,
0.1019301198, 0.0832767416, 0.0626720483, 0.0406014298, 0.0176140071,
0.0176140071, 0.0406014298, 0.0626720483, 0.0832767416, 0.1019301198,
0.1181945319, 0.1316886384, 0.1420961093, 0.1491729865, 0.1527533871
};
const double gauss_nodes[20] = {
-0.9931285992, -0.9639719273, -0.9122344283, -0.8391169718, -0.7463319065,
-0.6360536807, -0.5108670019, -0.3737060887, -0.2277858511, -0.0765265211,
0.0765265211, 0.2277858511, 0.3737060887, 0.5108670019, 0.6360536807,
0.7463319065, 0.8391169718, 0.9122344283, 0.9639719273, 0.9931285992
};
double sum_z = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
double weight = 0.5 * s * gauss_weights;
// Calculate the clothoid theta, kappa, sharpness at current s.
// Calculate the clothoid theta, kappa, sharpness at current s.
double sharpness10_i;
eq18_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10,gamma1,&sharpness10_i);
double kappa10_i;
eq19_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10_i,kappa10_i,gamma1,&kappa10_i);
double theta10_i;
eq20_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10_i,kappa10_i,theta10,gamma1,&theta10_i);
// Compute new coordinates using Gauss quadrature integration
double dz = sin(theta10_i) * weight;
sum_z += dz;
}
return z0 + sum_z - ze;
}
int
func_f (const gsl_vector * x, void *params, gsl_vector * f)
{
struct model_params *par = (struct model_params *) params;
double g11 = gsl_vector_get(x, 0);
double g21 = gsl_vector_get(x, 1);
double s1 = gsl_vector_get(x, 2);
double f1 = eq14_gauss_x(s1,
par->xs, par->xe,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21);
double f2 = eq14_gauss_y(s1,
par->ys, par->ye,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21);
double f3 = eq14_gauss_z(s1,
par->zs, par->ze,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21);
gsl_vector_set(f, 0, f1);
gsl_vector_set(f, 1, f2);
gsl_vector_set(f, 2, f3);
return GSL_SUCCESS;
}
int
func_df (const gsl_vector * x, void *params, gsl_matrix * J)
{
struct model_params *par = (struct model_params *) params;
double g_delta = 0.001;
double s_delta = 0.001;
double g11 = gsl_vector_get(x, 0);
double dg11 = g11 + g_delta;
double g21 = gsl_vector_get(x, 1);
double dg21 = g21 + g_delta;
double s1 = gsl_vector_get(x, 2);
double ds1 = s1 + s_delta;
// Jacobi 1. row
gsl_matrix_set(J, 0, 0, (eq14_gauss_x(s1,
par->xs, par->xe,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
dg11, g21) -
eq14_gauss_x(s1,
par->xs, par->xe,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / g_delta
);
gsl_matrix_set(J, 0, 1, (eq14_gauss_x(s1,
par->xs, par->xe,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, dg21) -
eq14_gauss_x(s1,
par->xs, par->xe,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / g_delta
);
gsl_matrix_set(J, 0, 2, (eq14_gauss_x(ds1,
par->xs, par->xe,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21) -
eq14_gauss_x(s1,
par->xs, par->xe,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / s_delta
);
// Jacobi 2. row
gsl_matrix_set(J, 1, 0, (eq14_gauss_y(s1,
par->ys, par->ye,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
dg11, g21) -
eq14_gauss_y(s1,
par->ys, par->ye,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / g_delta
);
gsl_matrix_set(J, 1, 1, (eq14_gauss_y(s1,
par->ys, par->ye,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, dg21) -
eq14_gauss_y(s1,
par->ys, par->ye,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / g_delta
);
gsl_matrix_set(J, 1, 2, (eq14_gauss_y(ds1,
par->ys, par->ye,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21) -
eq14_gauss_y(s1,
par->ys, par->ye,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / s_delta
);
// Jacobi 3. row
gsl_matrix_set(J, 2, 0, (eq14_gauss_z(s1,
par->zs, par->ze,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
dg11, g21) -
eq14_gauss_z(s1,
par->zs, par->ze,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / g_delta
);
gsl_matrix_set(J, 2, 1, (eq14_gauss_z(s1,
par->zs, par->ze,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, dg21) -
eq14_gauss_z(s1,
par->zs, par->ze,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / g_delta
);
gsl_matrix_set(J, 2, 2, (eq14_gauss_z(ds1,
par->zs, par->ze,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21) -
eq14_gauss_z(s1,
par->zs, par->ze,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / s_delta
);
return GSL_SUCCESS;
}
void
callback(const size_t iter, void *params,
const gsl_multifit_nlinear_workspace *w)
{
gsl_vector * x = gsl_multifit_nlinear_position(w);
double g11 = gsl_vector_get(x, 0);
double g21 = gsl_vector_get(x, 1);
double s1 = gsl_vector_get(x, 2);
/* print out current location */
printf("%f %f %f\n", g11, g21, s1);
}
void
solve_system(gsl_vector *x0, gsl_multifit_nlinear_fdf *fdf,
gsl_multifit_nlinear_parameters *params)
{
const gsl_multifit_nlinear_type *T = gsl_multifit_nlinear_trust;
const size_t max_iter = 200;
const double xtol = 1.0e-8;
const double gtol = 1.0e-8;
const double ftol = 1.0e-8;
const size_t n = fdf->n;
const size_t p = fdf->p;
gsl_multifit_nlinear_workspace *work =
gsl_multifit_nlinear_alloc(T, params, n, p);
gsl_vector * f = gsl_multifit_nlinear_residual(work);
gsl_vector * x = gsl_multifit_nlinear_position(work);
int info;
double chisq0, chisq, rcond;
printf("# %s/%s\n",
gsl_multifit_nlinear_name(work),
gsl_multifit_nlinear_trs_name(work));
/* initialize solver */
gsl_multifit_nlinear_init(x0, fdf, work);
/* store initial cost */
gsl_blas_ddot(f, f, &chisq0);
/* iterate until convergence */
gsl_multifit_nlinear_driver(max_iter, xtol, gtol, ftol,
callback, NULL, &info, work);
/* store final cost */
gsl_blas_ddot(f, f, &chisq);
/* store cond(J(x)) */
gsl_multifit_nlinear_rcond(&rcond, work);
printf("\n");
struct model_params *par = (struct model_params *) params;
double g11 = gsl_vector_get(x, 0);
double g21 = gsl_vector_get(x, 1);
double s1 = gsl_vector_get(x, 2);
double x_res = eq14_gauss_x(s1,
par->xs, par->xe,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21);
double y_res = eq14_gauss_y(s1,
par->ys, par->ye,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21);
double z_res = eq14_gauss_z(s1,
par->zs, par->ze,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21);
printf("Position Error: (%f %f %f)\n", x_res, y_res, z_res);
/* print summary */
fprintf(stderr, "%-25s %-6zu %-5zu %-5zu %-13.4e %-12.4e %-13.4e (%.2e, %.2e, %.2e)\n",
gsl_multifit_nlinear_trs_name(work),
gsl_multifit_nlinear_niter(work),
fdf->nevalf,
fdf->nevaldf,
chisq0,
chisq,
1.0 / rcond,
gsl_vector_get(x, 0),
gsl_vector_get(x, 1),
gsl_vector_get(x, 2));
printf("\n\n");
gsl_multifit_nlinear_free(work);
}
int
main (void)
{
const size_t n = 3;
const size_t p = 3;
gsl_vector *f = gsl_vector_alloc(n);
gsl_vector *x = gsl_vector_alloc(p);
gsl_multifit_nlinear_fdf fdf;
gsl_multifit_nlinear_parameters fdf_params =
gsl_multifit_nlinear_default_parameters();
struct model_params params;
params.t10 = 45.0 * (M_PI / 180.0);
params.t20 = 0.0 * (M_PI / 180.0);
params.k10 = 0.0;
params.k20 = 0.0;
params.c10 = 0.0;
params.c20 = 0.0;
params.xs = 0.0;
params.ys = 0.0;
params.zs = 0.0;
params.xe = 11.11;
params.ye = 22.22;
params.ze = 33.33;
params.xi;
params.yi;
params.zi;
/*
// print map of Phi(x1, x2)
{
double g11, g21, s1, chisq;
for (g11 = -5.0; g11 < 15.0; g11 += 0.1)
{
for (g21 = -5.0; g21 < 15.0; g21 += 0.1)
{
for (s1 = -5.0; s1 < 15.0; s1 += 0.1)
{
gsl_vector_set(x, 0, g11);
gsl_vector_set(x, 1, g21);
gsl_vector_set(x, 2, s1);
func_f(x, ¶ms, f);
gsl_blas_ddot(f, f, &chisq);
printf("%f %f %f %f\n", g11, g21, s1, chisq);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n\n");
}
/* define function to be minimized */
fdf.f = func_f;
fdf.df = func_df;
fdf.n = n;
fdf.p = p;
fdf.params = ¶ms;
/* starting point */
gsl_vector_set(x, 0, 0.01);
gsl_vector_set(x, 1, 0.01);
gsl_vector_set(x, 2, 0.01);
fprintf(stderr, "%-25s %-6s %-5s %-5s %-13s %-12s %-13s %-15s\n",
"Method", "NITER", "NFEV", "NJEV", "Initial Cost",
"Final cost", "Final cond(J)", "Final x");
fdf_params.trs = gsl_multifit_nlinear_trs_lm;
solve_system(x, &fdf, &fdf_params);
fdf_params.trs = gsl_multifit_nlinear_trs_dogleg;
solve_system(x, &fdf, &fdf_params);
fdf_params.trs = gsl_multifit_nlinear_trs_ddogleg;
solve_system(x, &fdf, &fdf_params);
fdf_params.trs = gsl_multifit_nlinear_trs_subspace2D;
solve_system(x, &fdf, &fdf_params);
gsl_vector_free(f);
gsl_vector_free(x);
return 0;
}
The idea was to calculate the elements of the Jacobian numerically but it fails miserably:
Warning: Spoiler!
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_vector.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_matrix.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_blas.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_multifit_nlinear.h>
/* eq18, page 4.
*
* stot = total clothoid length
* s = global length at clothoid to retrieve sharpness c.
*
* Retrieve the sharpness for s.
*
*/
void eq18(const double s, const double stot,
const double sharpnessi0, const double sharpnessi1, const double sharpnessi2, const double sharpnessi3,
const double yi1, const double yi2, const double yi3, const double yi4,
double *sharpness_at_s) {
double s1 = stot / 4.0;
double s2 = s1 + s1;
double s3 = s1 + s1 + s1;
double s4 = stot;
if (s <= s1) {
*sharpness_at_s = sharpnessi0 + yi1 * s;
} else if (s > s1 && s <= s2) {
*sharpness_at_s = sharpnessi1 + yi2 * (s - s1);
} else if (s > s2 && s <= s3) {
*sharpness_at_s = sharpnessi2 + yi3 * (s - s2);
} else if (s > s3 && s <= s4) {
*sharpness_at_s = sharpnessi3 + yi4 * (s - s3);
} else {
// Handle the case where s is out of bounds (optional)
*sharpness_at_s = 0.0; // or some other default value
printf("error: eq18. \n");
}
}
void eq18_single_clothoid(const double s,
const double sharpnessi0,
const double yi1,
double *sharpness_at_s) {
*sharpness_at_s = sharpnessi0 + yi1 * s;
}
/* eq19, page 4.
*
* stot = total clothoid length
* s = global length at clothoid to retrieve sharpness c.
*
* Retrieve the kappa for s.
*
*/
void eq19(const double s, const double stot,
const double sharpnessi0, const double sharpnessi1, const double sharpnessi2, const double sharpnessi3,
const double kappai0, const double kappai1, const double kappai2, const double kappai3,
const double yi1, const double yi2, const double yi3, const double yi4,
double *kappa_at_s) {
double s1 = stot / 4.0;
double s2 = s1 + s1;
double s3 = s1 + s1 + s1;
double s4 = stot;
if (s <= s1) {
*kappa_at_s = kappai0 + sharpnessi0 * s + 0.5 * yi1 * (s * s);
} else if (s > s1 && s <= s2) {
*kappa_at_s = kappai1 + sharpnessi1 * (s - s1) + 0.5 * yi2 * ((s - s1) * (s - s1));
} else if (s > s2 && s <= s3) {
*kappa_at_s = kappai2 + sharpnessi2 * (s - s2) + 0.5 * yi3 * ((s - s2) * (s - s2));
} else if (s > s3 && s <= s4) {
*kappa_at_s = kappai3 + sharpnessi3 * (s - s3) + 0.5 * yi4 * ((s - s3) * (s - s3));
} else {
// Handle the case where s is out of bounds (optional)
*kappa_at_s = 0.0; // or some other default value
printf("error: eq19. \n");
}
}
void eq19_single_clothoid(const double s,
const double sharpnessi0,
const double kappai0,
const double yi1,
double *kappa_at_s) {
*kappa_at_s = kappai0 + sharpnessi0 * s + 0.5 * yi1 * (s * s);
}
/* eq20, page 4.
*
* stot = total clothoid length
* s = global length at clothoid to retrieve sharpness c.
*
* Retrieve the theta at s.
*
*/
void eq20(const double s, const double stot,
const double sharpnessi0, const double sharpnessi1, const double sharpnessi2, const double sharpnessi3,
const double kappai0, const double kappai1, const double kappai2, const double kappai3,
const double thetai0, const double thetai1, const double thetai2, const double thetai3,
const double yi1, const double yi2, const double yi3, const double yi4,
double *theta_at_s) {
double s1 = stot / 4.0;
double s2 = s1 + s1;
double s3 = s1 + s1 + s1;
double s4 = stot;
if (s <= s1) {
*theta_at_s = thetai0 + kappai0 * s + (0.5*sharpnessi0) * (s * s) + (1.0 / 6.0) * yi1 * (s * s * s);
} else if (s > s1 && s <= s2) {
*theta_at_s = thetai1 + kappai1 * (s - s1) + (0.5*sharpnessi1) * ((s - s1) * (s - s1)) + (1.0 / 6.0) * yi2 * ((s - s1) * (s - s1) * (s - s1));
} else if (s > s2 && s <= s3) {
*theta_at_s = thetai2 + kappai2 * (s - s2) + (0.5*sharpnessi2) * ((s - s2) * (s - s2)) + (1.0 / 6.0) * yi3 * ((s - s2) * (s - s2) * (s - s2));
} else if (s > s3 && s <= s4) {
*theta_at_s = thetai3 + kappai3 * (s - s3) + (0.5*sharpnessi3) * ((s - s3) * (s - s3)) + (1.0 / 6.0) * yi4 * ((s - s3) * (s - s3) * (s - s3));
} else {
// Handle the case where s is out of bounds (optional)
*theta_at_s = 0.0; // or some other default value
printf("error: eq20.\n");
}
}
/* Get the theta given s (length) for a single clothoid.
*
*/
void eq20_single_clothoid(const double s,
const double sharpnessi0,
const double kappai0,
const double thetai0,
const double yi1,
double *theta_at_s) {
*theta_at_s = thetai0 + kappai0 * s + (0.5*sharpnessi0) * (s * s) + (1.0 / 6.0) * yi1 * (s * s * s);
}
/* parameters to model */
struct model_params
{
double t10;
double t20;
double k10;
double k20;
double c10;
double c20;
double xs;
double ys;
double zs;
double xe;
double ye;
double ze;
double xi;
double yi;
double zi;
};
/* eq14, page 4
*
* Most efficient and precise solution to compute the clothoid curve lenght.
* Using gauss legendre, up to 20 points. Use a 30 point legendre to get even
* more accuracy.
*
* This calculation is more accurate then the above eq14_drift function.
*
* s = lenght on clothoid to retrieve the xyz point, xi,yi,zi.
* x0 y0 z0 = Clothoid start point.
* ltot = Clothoid length up to s.
*
* gamma1, gamma2, clothoid's rigid body factor. Synonims for y11, y22.
*
*/
float eq14_gauss_x(double s,
double x0, double xe,
double theta10, double theta20,
double kappa10, double kappa20,
double sharpness10, double sharpness20,
double gamma1, double gamma2) {
// Gauss-Legendre 20-point weights & nodes
const double gauss_weights[20] = {
0.1527533871, 0.1491729865, 0.1420961093, 0.1316886384, 0.1181945319,
0.1019301198, 0.0832767416, 0.0626720483, 0.0406014298, 0.0176140071,
0.0176140071, 0.0406014298, 0.0626720483, 0.0832767416, 0.1019301198,
0.1181945319, 0.1316886384, 0.1420961093, 0.1491729865, 0.1527533871
};
const double gauss_nodes[20] = {
-0.9931285992, -0.9639719273, -0.9122344283, -0.8391169718, -0.7463319065,
-0.6360536807, -0.5108670019, -0.3737060887, -0.2277858511, -0.0765265211,
0.0765265211, 0.2277858511, 0.3737060887, 0.5108670019, 0.6360536807,
0.7463319065, 0.8391169718, 0.9122344283, 0.9639719273, 0.9931285992
};
double sum_x = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
double weight = 0.5 * s * gauss_weights;
// Calculate the clothoid theta, kappa, sharpness at current s.
double sharpness10_i;
eq18_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10,gamma1,&sharpness10_i);
double sharpness20_i;
eq18_single_clothoid(0,sharpness20,gamma2,&sharpness20_i);
double kappa10_i;
eq19_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10_i,kappa10_i,gamma1,&kappa10_i);
double kappa20_i;
eq19_single_clothoid(0,sharpness20_i,kappa20_i,gamma2,&kappa20_i);
double theta10_i;
eq20_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10_i,kappa10_i,theta10,gamma1,&theta10_i);
double theta20_i;
eq20_single_clothoid(0,sharpness20_i,kappa20_i,theta20,gamma2,&theta20_i);
// Compute new coordinates using Gauss quadrature integration
double dx = cos(theta10_i) * cos(theta20_i) * weight;
sum_x += dx;
}
return x0 + sum_x - xe;
}
float eq14_gauss_y(double s,
double y0, double ye,
double theta10, double theta20,
double kappa10, double kappa20,
double sharpness10, double sharpness20,
double gamma1, double gamma2) {
// Gauss-Legendre 20-point weights & nodes
const double gauss_weights[20] = {
0.1527533871, 0.1491729865, 0.1420961093, 0.1316886384, 0.1181945319,
0.1019301198, 0.0832767416, 0.0626720483, 0.0406014298, 0.0176140071,
0.0176140071, 0.0406014298, 0.0626720483, 0.0832767416, 0.1019301198,
0.1181945319, 0.1316886384, 0.1420961093, 0.1491729865, 0.1527533871
};
const double gauss_nodes[20] = {
-0.9931285992, -0.9639719273, -0.9122344283, -0.8391169718, -0.7463319065,
-0.6360536807, -0.5108670019, -0.3737060887, -0.2277858511, -0.0765265211,
0.0765265211, 0.2277858511, 0.3737060887, 0.5108670019, 0.6360536807,
0.7463319065, 0.8391169718, 0.9122344283, 0.9639719273, 0.9931285992
};
double sum_y = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
double weight = 0.5 * s * gauss_weights;
// Calculate the clothoid theta, kappa, sharpness at current s.
double sharpness10_i;
eq18_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10,gamma1,&sharpness10_i);
double sharpness20_i;
eq18_single_clothoid(0,sharpness20,gamma2,&sharpness20_i);
double kappa10_i;
eq19_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10_i,kappa10_i,gamma1,&kappa10_i);
double kappa20_i;
eq19_single_clothoid(0,sharpness20_i,kappa20_i,gamma2,&kappa20_i);
double theta10_i;
eq20_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10_i,kappa10_i,theta10,gamma1,&theta10_i);
double theta20_i;
eq20_single_clothoid(0,sharpness20_i,kappa20_i,theta20,gamma2,&theta20_i);
// Compute new coordinates using Gauss quadrature integration
double dy = cos(theta10_i) * sin(theta20_i) * weight;
sum_y += dy;
}
return y0 + sum_y - ye;
}
float eq14_gauss_z(double s,
double z0, double ze,
double theta10, double theta20,
double kappa10, double kappa20,
double sharpness10, double sharpness20,
double gamma1, double gamma2) {
// Gauss-Legendre 20-point weights & nodes
const double gauss_weights[20] = {
0.1527533871, 0.1491729865, 0.1420961093, 0.1316886384, 0.1181945319,
0.1019301198, 0.0832767416, 0.0626720483, 0.0406014298, 0.0176140071,
0.0176140071, 0.0406014298, 0.0626720483, 0.0832767416, 0.1019301198,
0.1181945319, 0.1316886384, 0.1420961093, 0.1491729865, 0.1527533871
};
const double gauss_nodes[20] = {
-0.9931285992, -0.9639719273, -0.9122344283, -0.8391169718, -0.7463319065,
-0.6360536807, -0.5108670019, -0.3737060887, -0.2277858511, -0.0765265211,
0.0765265211, 0.2277858511, 0.3737060887, 0.5108670019, 0.6360536807,
0.7463319065, 0.8391169718, 0.9122344283, 0.9639719273, 0.9931285992
};
double sum_z = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
double weight = 0.5 * s * gauss_weights;
// Calculate the clothoid theta, kappa, sharpness at current s.
// Calculate the clothoid theta, kappa, sharpness at current s.
double sharpness10_i;
eq18_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10,gamma1,&sharpness10_i);
double kappa10_i;
eq19_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10_i,kappa10_i,gamma1,&kappa10_i);
double theta10_i;
eq20_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10_i,kappa10_i,theta10,gamma1,&theta10_i);
// Compute new coordinates using Gauss quadrature integration
double dz = sin(theta10_i) * weight;
sum_z += dz;
}
return z0 + sum_z - ze;
}
int
func_f (const gsl_vector * x, void *params, gsl_vector * f)
{
struct model_params *par = (struct model_params *) params;
double g11 = gsl_vector_get(x, 0);
double g21 = gsl_vector_get(x, 1);
double s1 = gsl_vector_get(x, 2);
double f1 = eq14_gauss_x(s1,
par->xs, par->xe,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21);
double f2 = eq14_gauss_y(s1,
par->ys, par->ye,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21);
double f3 = eq14_gauss_z(s1,
par->zs, par->ze,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21);
gsl_vector_set(f, 0, f1);
gsl_vector_set(f, 1, f2);
gsl_vector_set(f, 2, f3);
return GSL_SUCCESS;
}
int
func_df (const gsl_vector * x, void *params, gsl_matrix * J)
{
struct model_params *par = (struct model_params *) params;
double g_delta = 0.001;
double s_delta = 0.001;
double g11 = gsl_vector_get(x, 0);
double dg11 = g11 + g_delta;
double g21 = gsl_vector_get(x, 1);
double dg21 = g21 + g_delta;
double s1 = gsl_vector_get(x, 2);
double ds1 = s1 + s_delta;
// Jacobi 1. row
gsl_matrix_set(J, 0, 0, (eq14_gauss_x(s1,
par->xs, par->xe,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
dg11, g21) -
eq14_gauss_x(s1,
par->xs, par->xe,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / g_delta
);
gsl_matrix_set(J, 0, 1, (eq14_gauss_x(s1,
par->xs, par->xe,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, dg21) -
eq14_gauss_x(s1,
par->xs, par->xe,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / g_delta
);
gsl_matrix_set(J, 0, 2, (eq14_gauss_x(ds1,
par->xs, par->xe,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21) -
eq14_gauss_x(s1,
par->xs, par->xe,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / s_delta
);
// Jacobi 2. row
gsl_matrix_set(J, 1, 0, (eq14_gauss_y(s1,
par->ys, par->ye,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
dg11, g21) -
eq14_gauss_y(s1,
par->ys, par->ye,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / g_delta
);
gsl_matrix_set(J, 1, 1, (eq14_gauss_y(s1,
par->ys, par->ye,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, dg21) -
eq14_gauss_y(s1,
par->ys, par->ye,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / g_delta
);
gsl_matrix_set(J, 1, 2, (eq14_gauss_y(ds1,
par->ys, par->ye,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21) -
eq14_gauss_y(s1,
par->ys, par->ye,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / s_delta
);
// Jacobi 3. row
gsl_matrix_set(J, 2, 0, (eq14_gauss_z(s1,
par->zs, par->ze,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
dg11, g21) -
eq14_gauss_z(s1,
par->zs, par->ze,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / g_delta
);
gsl_matrix_set(J, 2, 1, (eq14_gauss_z(s1,
par->zs, par->ze,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, dg21) -
eq14_gauss_z(s1,
par->zs, par->ze,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / g_delta
);
gsl_matrix_set(J, 2, 2, (eq14_gauss_z(ds1,
par->zs, par->ze,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21) -
eq14_gauss_z(s1,
par->zs, par->ze,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21)) / s_delta
);
return GSL_SUCCESS;
}
void
callback(const size_t iter, void *params,
const gsl_multifit_nlinear_workspace *w)
{
gsl_vector * x = gsl_multifit_nlinear_position(w);
double g11 = gsl_vector_get(x, 0);
double g21 = gsl_vector_get(x, 1);
double s1 = gsl_vector_get(x, 2);
/* print out current location */
printf("%f %f %f\n", g11, g21, s1);
}
void
solve_system(gsl_vector *x0, gsl_multifit_nlinear_fdf *fdf,
gsl_multifit_nlinear_parameters *params)
{
const gsl_multifit_nlinear_type *T = gsl_multifit_nlinear_trust;
const size_t max_iter = 200;
const double xtol = 1.0e-8;
const double gtol = 1.0e-8;
const double ftol = 1.0e-8;
const size_t n = fdf->n;
const size_t p = fdf->p;
gsl_multifit_nlinear_workspace *work =
gsl_multifit_nlinear_alloc(T, params, n, p);
gsl_vector * f = gsl_multifit_nlinear_residual(work);
gsl_vector * x = gsl_multifit_nlinear_position(work);
int info;
double chisq0, chisq, rcond;
printf("# %s/%s\n",
gsl_multifit_nlinear_name(work),
gsl_multifit_nlinear_trs_name(work));
/* initialize solver */
gsl_multifit_nlinear_init(x0, fdf, work);
/* store initial cost */
gsl_blas_ddot(f, f, &chisq0);
/* iterate until convergence */
gsl_multifit_nlinear_driver(max_iter, xtol, gtol, ftol,
callback, NULL, &info, work);
/* store final cost */
gsl_blas_ddot(f, f, &chisq);
/* store cond(J(x)) */
gsl_multifit_nlinear_rcond(&rcond, work);
printf("\n");
struct model_params *par = (struct model_params *) params;
double g11 = gsl_vector_get(x, 0);
double g21 = gsl_vector_get(x, 1);
double s1 = gsl_vector_get(x, 2);
double x_res = eq14_gauss_x(s1,
par->xs, par->xe,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21);
double y_res = eq14_gauss_y(s1,
par->ys, par->ye,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21);
double z_res = eq14_gauss_z(s1,
par->zs, par->ze,
par->t10, par->t20,
par->k10, par->k20,
par->c10, par->c20,
g11, g21);
printf("Position Error: (%f %f %f)\n", x_res, y_res, z_res);
/* print summary */
fprintf(stderr, "%-25s %-6zu %-5zu %-5zu %-13.4e %-12.4e %-13.4e (%.2e, %.2e, %.2e)\n",
gsl_multifit_nlinear_trs_name(work),
gsl_multifit_nlinear_niter(work),
fdf->nevalf,
fdf->nevaldf,
chisq0,
chisq,
1.0 / rcond,
gsl_vector_get(x, 0),
gsl_vector_get(x, 1),
gsl_vector_get(x, 2));
printf("\n\n");
gsl_multifit_nlinear_free(work);
}
int
main (void)
{
const size_t n = 3;
const size_t p = 3;
gsl_vector *f = gsl_vector_alloc(n);
gsl_vector *x = gsl_vector_alloc(p);
gsl_multifit_nlinear_fdf fdf;
gsl_multifit_nlinear_parameters fdf_params =
gsl_multifit_nlinear_default_parameters();
struct model_params params;
params.t10 = 45.0 * (M_PI / 180.0);
params.t20 = 0.0 * (M_PI / 180.0);
params.k10 = 0.0;
params.k20 = 0.0;
params.c10 = 0.0;
params.c20 = 0.0;
params.xs = 0.0;
params.ys = 0.0;
params.zs = 0.0;
params.xe = 11.11;
params.ye = 22.22;
params.ze = 33.33;
params.xi;
params.yi;
params.zi;
/*
// print map of Phi(x1, x2)
{
double g11, g21, s1, chisq;
for (g11 = -5.0; g11 < 15.0; g11 += 0.1)
{
for (g21 = -5.0; g21 < 15.0; g21 += 0.1)
{
for (s1 = -5.0; s1 < 15.0; s1 += 0.1)
{
gsl_vector_set(x, 0, g11);
gsl_vector_set(x, 1, g21);
gsl_vector_set(x, 2, s1);
func_f(x, ¶ms, f);
gsl_blas_ddot(f, f, &chisq);
printf("%f %f %f %f\n", g11, g21, s1, chisq);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n\n");
}
/* define function to be minimized */
fdf.f = func_f;
fdf.df = func_df;
fdf.n = n;
fdf.p = p;
fdf.params = ¶ms;
/* starting point */
gsl_vector_set(x, 0, 0.01);
gsl_vector_set(x, 1, 0.01);
gsl_vector_set(x, 2, 0.01);
fprintf(stderr, "%-25s %-6s %-5s %-5s %-13s %-12s %-13s %-15s\n",
"Method", "NITER", "NFEV", "NJEV", "Initial Cost",
"Final cost", "Final cond(J)", "Final x");
fdf_params.trs = gsl_multifit_nlinear_trs_lm;
solve_system(x, &fdf, &fdf_params);
fdf_params.trs = gsl_multifit_nlinear_trs_dogleg;
solve_system(x, &fdf, &fdf_params);
fdf_params.trs = gsl_multifit_nlinear_trs_ddogleg;
solve_system(x, &fdf, &fdf_params);
fdf_params.trs = gsl_multifit_nlinear_trs_subspace2D;
solve_system(x, &fdf, &fdf_params);
gsl_vector_free(f);
gsl_vector_free(x);
return 0;
}
The idea was to calculate the elements of the Jacobian numerically but it fails miserably:
- Aciera

21 Feb 2025 09:40
Replied by Aciera on topic scurve trajectory planner
scurve trajectory planner
Category: General LinuxCNC Questions
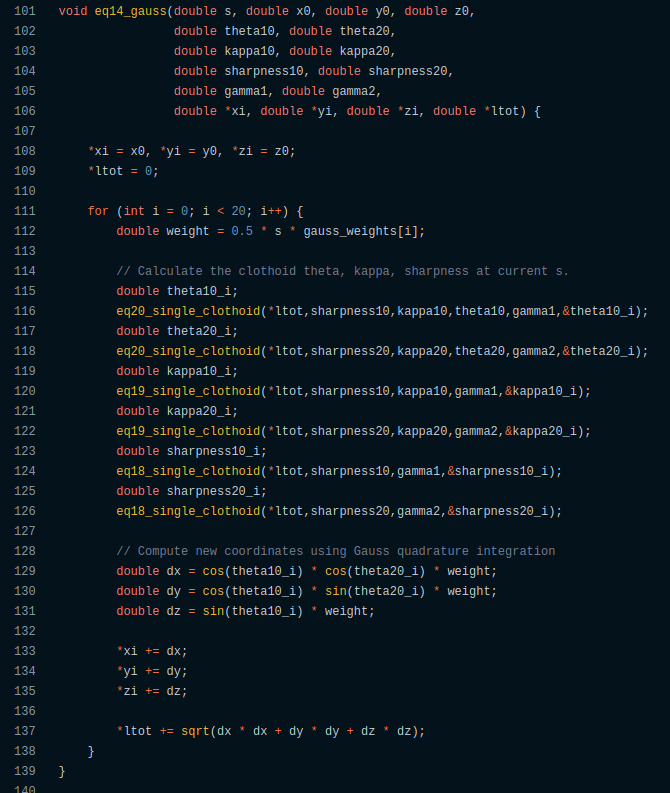
Something like this:
// Calculate the clothoid theta, kappa, sharpness at current s.
double sharpness10_i;
eq18_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10,gamma1,&sharpness10_i);
double sharpness20_i;
eq18_single_clothoid(0,sharpness20,gamma2,&sharpness20_i);
double kappa10_i;
eq19_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10_i,kappa10_i,gamma1,&kappa10_i);
double kappa20_i;
eq19_single_clothoid(0,sharpness20_i,kappa20_i,gamma2,&kappa20_i);
double theta10_i;
eq20_single_clothoid(0,sharpness10_i,kappa10_i,theta10,gamma1,&theta10_i);
double theta20_i;
eq20_single_clothoid(0,sharpness20_i,kappa20_i,theta20,gamma2,&theta20_i);- Aciera

21 Feb 2025 09:30 - 21 Feb 2025 09:44
Replied by Aciera on topic scurve trajectory planner
scurve trajectory planner
Category: General LinuxCNC Questions
- Vector

21 Feb 2025 09:00
Replied by Vector on topic Red Machine Outline is backwards in Y dimension
Red Machine Outline is backwards in Y dimension
Category: Qtvcp
Oh, and also, the GEOMETRY = XYZBC, no need for that -Y.
- Vector

21 Feb 2025 08:55
Replied by Vector on topic Red Machine Outline is backwards in Y dimension
Red Machine Outline is backwards in Y dimension
Category: Qtvcp
OK, alright, for anyone who finds this, and has the same cognitive block I did, here's my answer and hopefully it helps you.
Right hand rule: (as Rob has pointed out many times), um rules: so...
Top of Machine is low negative, and gets more negative as you go down.
Left of machine is zero, and gets more positive as you go right
Back of machine is High Positive, and gets more negative as you come forward (this was my Y axis and my first sticking point)
Depending on wiring and screw shafts and belts and whatever, you have to determine which way to move your axis so that it obeys that convention.
A test with writing will help, since it will be mirrored in some direction if you have your motors going the wrong way.
See: ~/linuxcnc/nc_files/examples/3dtest.ngc and /usr/share/axis/images/axis.ngc
To reverse a motor/axis (I needed to do this to get myself right: I was 'writing' the logo mirror-backwards in Y) the easiest thing is to go to your .ini file, to the [JOINT_n] for your axis, and reverse the sign on STEP_SCALE. (There are other ways, reversing wiring, etc, but this worked for me and is easy to undo and all my wiring was otherwise identical, so I preferred a software solution.)
Then you need to worry about homing. If you had it working before (as I did) then you'll need to reverse the signs on HOME_SEARCH_VEL and HOME_LATCH_VEL (Mine went from positive to negative).
Finally, and this is the one that bent me a bit. (And I see Aciera has jumped in to help me while I'm writing this, and I thank him very much, but I don't think the answer is quite right for me... I tried that and it wasn't very good.)
You have to make sure you're honoring the right-hand-rule, which means whereever your sensor is that trips to signal your axis has reached it during homeing, should be numbered accordingly.
The part I had to wrap my brain around was that in my case, this means it's:
I was trying all kinds of HOME_OFFSET settings waaay too close to zero.
Now my machine red lines are correct, and loaded files show inside the machine, and all the axes move the way they're supposed to.
It even 'air carves' LinuxCNC as pretty as can be.
Thank you thank you Aciera!
Cheers everyone!
Right hand rule: (as Rob has pointed out many times), um rules: so...
Top of Machine is low negative, and gets more negative as you go down.
Left of machine is zero, and gets more positive as you go right
Back of machine is High Positive, and gets more negative as you come forward (this was my Y axis and my first sticking point)
Depending on wiring and screw shafts and belts and whatever, you have to determine which way to move your axis so that it obeys that convention.
A test with writing will help, since it will be mirrored in some direction if you have your motors going the wrong way.
See: ~/linuxcnc/nc_files/examples/3dtest.ngc and /usr/share/axis/images/axis.ngc
To reverse a motor/axis (I needed to do this to get myself right: I was 'writing' the logo mirror-backwards in Y) the easiest thing is to go to your .ini file, to the [JOINT_n] for your axis, and reverse the sign on STEP_SCALE. (There are other ways, reversing wiring, etc, but this worked for me and is easy to undo and all my wiring was otherwise identical, so I preferred a software solution.)
Then you need to worry about homing. If you had it working before (as I did) then you'll need to reverse the signs on HOME_SEARCH_VEL and HOME_LATCH_VEL (Mine went from positive to negative).
Finally, and this is the one that bent me a bit. (And I see Aciera has jumped in to help me while I'm writing this, and I thank him very much, but I don't think the answer is quite right for me... I tried that and it wasn't very good.)
You have to make sure you're honoring the right-hand-rule, which means whereever your sensor is that trips to signal your axis has reached it during homeing, should be numbered accordingly.
The part I had to wrap my brain around was that in my case, this means it's:
HOME_OFFSET = 300
HOME = 290
MIN_LIMIT=0
MAX_LIMIT=300I was trying all kinds of HOME_OFFSET settings waaay too close to zero.
Now my machine red lines are correct, and loaded files show inside the machine, and all the axes move the way they're supposed to.
It even 'air carves' LinuxCNC as pretty as can be.
Thank you thank you Aciera!
Cheers everyone!
- tcbmetalworks
- tcbmetalworks
21 Feb 2025 08:32
Replied by tcbmetalworks on topic Toyoda FHN80T
Toyoda FHN80T
Category: CNC Machines
Did you ever end up finishing this project?
- Hakan
- Hakan
21 Feb 2025 07:14
Replied by Hakan on topic EtherCAT plasma torch voltage reader
EtherCAT plasma torch voltage reader
Category: Show Your Stuff
It can be done pretty easily with external components.
Feed 24V using the unused leads in the CAT cable, and a step-down unit from 24V to 5V and there you have it.
At the prototype stage this simple cable will work. And 24V stepdown converter (board needs 5V) is dirt cheap.
BTW the photo-diode opens so good that I don't need a torch-on relay, but can be had if needed.
Feed 24V using the unused leads in the CAT cable, and a step-down unit from 24V to 5V and there you have it.
At the prototype stage this simple cable will work. And 24V stepdown converter (board needs 5V) is dirt cheap.
BTW the photo-diode opens so good that I don't need a torch-on relay, but can be had if needed.
- azim4411
- azim4411
21 Feb 2025 07:08
Replied by azim4411 on topic Elumatec SBZ 130/01 retrofit
Elumatec SBZ 130/01 retrofit
Category: CNC Machines
Dear tommylight,
I sincerely apologize for taking your support for granted without doing my own due diligence, so I went back and read the entire thread from start to finish to enhance my understanding a bit better before asking anything else. Unfortunately, I am a student with little to no prior experience within this field (mesa, linuxcnc, machinery). While I understand everyone here is quite busy and their time is invaluable, I would wholeheartedly appreciate some guidance from experts like yourself. I also spent a lot of time reviewing the wiring diagram as well as physically cross-referencing things with the actual machine, which helped my insight quite a lot, however, I also have ended up with many many more questions.
1) I have confirmed how the ATC operates, it uses the same 4-switch grayscale sensor within the gearbox to check in position as well as indexing, however, the actual motion requires the spindle to be 'straight' so that the tool ends can slide into a locking area, at first I expected this to be done by the absolute encoder, since there's no sensors or anything for reference gtgrips in the spindle system, however after checking the wiring and the DARC manuals, they are listed as 'resolver' cables, specifically 2 pole resolvers which as far as I have seen, cannot perform this function, please let me know if otherwise.
2) the same is true for ALL the axis motors, except the long X axis, (no short X axis in this machine, 2001/2003 model sbz 130/01, but everything else looks the same as yours ), but only the X axis I have found some sort of spring based limit switch that can be seen for referencing trips, but I have also reason to believe these might just be for emergency and is it possible these resolvers can be used as absolute encoder functions (no homing).
3) after some research into Linuxcnc and mesa cards configuration, I have understood the choice of your mesa cards (input cards, output, analog control for the servos, FGPA card, connector, etc) however I would like to know how compatible your set of files/card combination would be in this case for me.
Once again I am deeply sorry for my earlier ignorance, it is simply my lack of experience, and I would really appreciate some guidance in these questions as well as my future doubts, and I will do my best to be vigilant in my own education on the matter.
I sincerely apologize for taking your support for granted without doing my own due diligence, so I went back and read the entire thread from start to finish to enhance my understanding a bit better before asking anything else. Unfortunately, I am a student with little to no prior experience within this field (mesa, linuxcnc, machinery). While I understand everyone here is quite busy and their time is invaluable, I would wholeheartedly appreciate some guidance from experts like yourself. I also spent a lot of time reviewing the wiring diagram as well as physically cross-referencing things with the actual machine, which helped my insight quite a lot, however, I also have ended up with many many more questions.
1) I have confirmed how the ATC operates, it uses the same 4-switch grayscale sensor within the gearbox to check in position as well as indexing, however, the actual motion requires the spindle to be 'straight' so that the tool ends can slide into a locking area, at first I expected this to be done by the absolute encoder, since there's no sensors or anything for reference gtgrips in the spindle system, however after checking the wiring and the DARC manuals, they are listed as 'resolver' cables, specifically 2 pole resolvers which as far as I have seen, cannot perform this function, please let me know if otherwise.
2) the same is true for ALL the axis motors, except the long X axis, (no short X axis in this machine, 2001/2003 model sbz 130/01, but everything else looks the same as yours ), but only the X axis I have found some sort of spring based limit switch that can be seen for referencing trips, but I have also reason to believe these might just be for emergency and is it possible these resolvers can be used as absolute encoder functions (no homing).
3) after some research into Linuxcnc and mesa cards configuration, I have understood the choice of your mesa cards (input cards, output, analog control for the servos, FGPA card, connector, etc) however I would like to know how compatible your set of files/card combination would be in this case for me.
Once again I am deeply sorry for my earlier ignorance, it is simply my lack of experience, and I would really appreciate some guidance in these questions as well as my future doubts, and I will do my best to be vigilant in my own education on the matter.
Time to create page: 0.636 seconds